The AQA requires the students to understand genetic engineering and the advantages it can offer. The students need to ensure they know the process of inserting a gene into a bacterium.
The AQA specification states
”
d) In genetic engineering, genes from the chromosomes of humans and other organisms can be ‘cut out’ using enzymes and transferred to cells of other organisms.
e) Genes can also be transferred to the cells of animals, plants or microorganisms at an early stage in their development so that they develop with desired characteristics.
– new genes can be transferred to crop plants
– crops that have had their genes modified in this way are called genetically modified crops (GM crops)
– examples of genetically modified crops include ones that are resistant to insect attack or to herbicides.
– genetically modified crops generally show increased yields.
f) Concerns about GM crops include the effect on populations of wild flowers and insects, and uncertainty about the effects of eating GM crops on human health.”
So what is genetic engineering?
Is a scientific technique that changes the genetic material of an organism. The gene is taken from one organism and transferred to another. Genes from the chromosomes of a human cell can be ‘cut out’ using enzymes and is transferred to the cell of a bacterium.
The classic example of genetic engineering is Insulin production by bacteria using the human gene.
The basic principle is that the human gene for insulin creation is ‘cut out’ from human cell. This uses an enzymes that cuts out the gene ready to be inserted into a bacterium. The process is best summarised using a diagram.
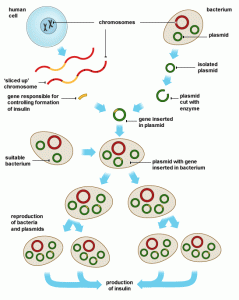 Source BBC Bitesize. Genetic engineering.
Source BBC Bitesize. Genetic engineering.
Transferring genes to both animals and plants.
Genes provide the instructions to make a particular protein. If a gene is inserted into an organism at an early stage of their development. As the organisms develops with the new desired characteristics from the other organism. Lots of examples of the use of genetic engineering can be found through a simple web search for example
Other benefits include
– creating the hormone insulin by genetically engineered bacteria.
– improve growth rate of plants and animals.
– crops normally have a larger yield.
– can be designed to grow in hot, dry or cold conditions.
– crop resistant.
New medicine “human engineering’
A growing field of medicine and science is genetic engineering. We are hopeful that diseases may be cured by placing healthy genes into cells. If this technique become possible it may be possible to cure children of life threatening illnesses and disease.
Problems with genetic engineering.
This is a new field of research “genetic engineering’ is both promising and poses many ethical issues. Some of the problems include
– hard to predict long term effects
– insects may become pesticide-resistant if they eat a constant diet of pesticide-forming plants.
– genes from genetically modified plants and animals might spread into the wildlife of the countryside
– GM crops are often infertile, which means farmers in poor countries have to buy new seed each year.
– Ethics of designer babies.
